Types of Folds
An Illustrated Tutorial from "Drawing People: How to Portray the Clothed Figure"
by Barbara Bradley
Breaking
down the types of folds into categories may seem removed from the
purpose of drawing folds on people. But to be in control of the folds
you draw, you have to know the characteristics of each type so you can
recognize and use them to your advantage, blending them into a
harmonious whole.
|
Pipe
Zigzag
Spiral
|
Half-Lock
Diaper
|
Drop
Inert |
|
|
|
|
|
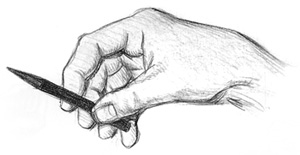
Use a Sharp, Soft Medium - I
recommend a soft stick medium, such as X-soft compressed charcoal or a
pastel stick in a dark brown color. Conte Bistre is a good choice. To
sharpen it, make a long point on your medium with a craft knife, then
smooth its sides on a sand pad so you have the choice of making a line
using the tip of the medium or apply tone using the side.
|
Hold Your Medium Overhand -
Let this be an order! Hold your medium overhand so you can apply
strokes in any direction. With your palm upward, place the drawing
medium perpendicular, not parallel, to the line of your fingers. As you
draw, make sure it continues to lie across your fingers. If your medium
is parallel to your fingers, it will get "stuck" and you won't be able
to stroke in as many directions or change from line to tone. |
|
|
|
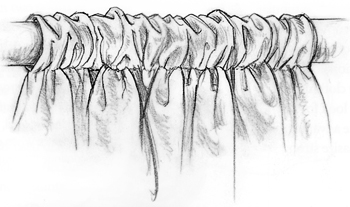
PIPE FOLDS
In
their most regular pattern, pipe folds resemble a series of organ
pipes, thus their name. Their shapes may be semi-cylindrical or
semi-conical. You see them everywhere from clothing to drapery. There
are two varieties of pipe folds: relaxed and stretched.
|
|
|
|
|
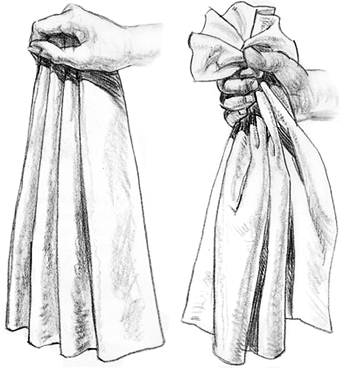
Relaxed Pipe Folds - You
see this type of pipe fold when fabric falls freely from a condensed
area. Arrange a short end of a rectangle of cloth into pleats, grasping
it at the top and letting the remaining fabric fall. These pipe folds,
semi-cylindrical in shape and consistent in size, are the type you see
in formal window draperies [above left]. To study irregular pipe folds
[above right], gather the material toward the top before letting the
rest of the material fall. These pipe folds are semi-conical in shape
and vary more in size. Fabric gathered in waistbands shows this kind of
fold.
|
Stretched Pipe Folds -
Fold a square of cloth into a triangle. Gather it near the upper
corners and pull. This creates the cordlike pipe folds that appear in
stretched fabric. You can also see these folds in rectangular fabric
that has been gathered and pulled. However diagonal fabric stretches
more. |
|
| ZIGZAG FOLDS
Zigzag
refers to the pattern of alternating folds that occurs on the inside of
the bend of a tubular piece of fabric when the fabric buckles. To see
zigzag folds, put on a jacket, put you hand in the pocket to bend your
arm a bit and look in a mirror. When the tubular piece of cloth that
makes up your sleeve bends, the stretching side of the cloth along the
back of your arm becomes taut while the excess fabric on the inside
buckles.
|
|
|
|
|
What Makes a Zigzag Fold?
Zigzag folds alternate directions. The nature of fabric affects the folds, the stiffer the fabric, the more angular the folds. |
Planes of ZigZag Folds
Notice
the horizontal diamond shapes. The top and bottom of each diamond fold
toward each other to form two triangular planes meeting in the middle.
Because the planes face different directions, each receives light
differently. |
Memory Zigzag Folds
This
woman's knees are locked, not bent, but the cloth of her jeans has been
bent so often that the folds have left an imprint. Study people waiting
in line or standing on public transit. At the back of the knees of
well-worn pants, you often see such zigzag folds caused by frequent
compressions from bending the knees. |
|
|
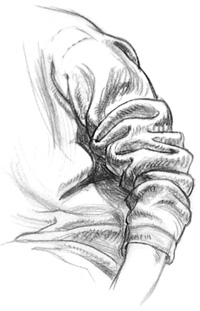
| SPIRAL FOLDS
Spiral
folds result when tubular pieces of cloth condense around tubular
forms, such as a sleeve around an arm. Different gestures cause
different directions of spiral folds, and variables like the amount and
character of the fabric affect the number of folds that form. The more
fabric condensed into one area, the more folds appear. The softer the
fabric, the more typically rounded are the spirals.
Spirals Form Around Cylinders
Cloth wrapped around curtain rods exhibits
spiral folds. Notice the pipe folds that fall from the rod. Elastic in
clothing, such as waistbands, creates similar but small spiral folds.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Condensed Fabric - Push
the sleeve of a sweatshirt or soft sweater up your arm, condensing the
fabric. Most of these folds actually form only partial spirals that
don't go all the way around the form.
|
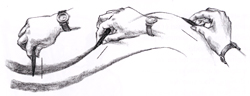
Direction Relates to Tension - The
direction of spiral folds relates to the gesture of the underlying
form. The tension between the armpit and elbow causes folds that travel
diagonally between the two.
|
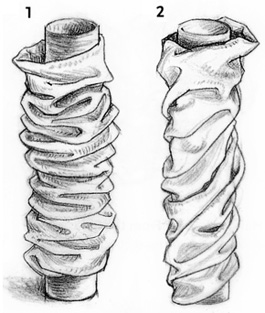
Create These Effects Yourself - You
can make spiral folds by inserting a cardboard cylinder into a longer
piece of fabric, with the edges stapled together to form a cylinder.
Soft cotton (drawing 1) makes typically rounded spiral folds. If you
twist the fabric as you condense it (drawing 2), the folds spiral
diagonally.
|
|
|
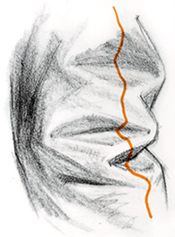
HALF-LOCK FOLDS
Half-lock
folds occur when tubular pieces of cloth abruptly change direction.
When a part of the figure abruptly changes direction, look for
corresponding parts of the clothing that change direction. Then look
for half-lock folds in these areas. Take advantage of half-lock folds
to emphasize strong changes of direction.
|
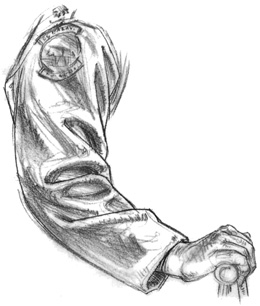 |
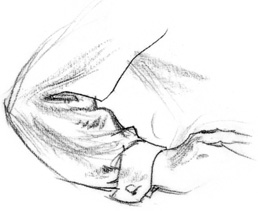
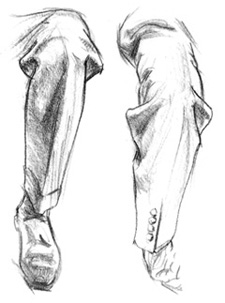
Wrap Folds Around Outside Edges - Two
half-lock folds appear at the bend of the inner arm in this drawing.
Sometimes you'll see multiple half-lock folds, and somtimes you'll see a
smaller half-lock inside a larger one. To make half-lock folds or any
other fold look natural, pay attention to the way it wraps around the
forms underneath. When drawing a fold as it wraps around a form,
remember to continue the wraparound to the outer edge.
|
|
|
|
|
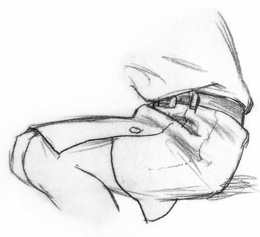
| Half-Lock Folds From the Side - Half-lock folds are most obvious from the side. You can easily see them on sharply bent legs, arms and torsos. |
|
|
Half-Lock Folds From the Front
The bulges of half-lock folds are visible
on the sides of knees and elbows from a
front view. |
|
|
| DIAPER FOLDS
Diaper
folds form when fabric sags between two points of support. Folds form
in directions that radiate from each point and meet between them. The
low point of the sag where each fold meets the other may curve or bend
sharply. The degree of the bend or curve depends on the amount of slack
and the character of the fabric. The crisper a fabric is, the more
angular is the break.
Classical,
Byzantine and early medieval artists used diaper folds beautifully.
Look for them particularly in clocks, necklines and the slack areas
between the knees of Madonas, saints, angels and royalty.
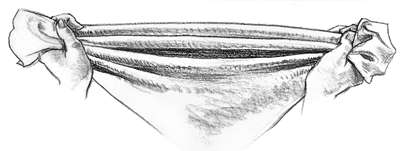
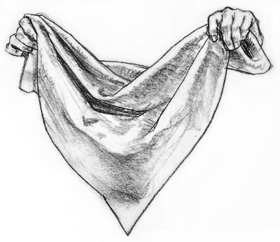
Sagging Fabric
Hold
a piece of fabric by the upper corners and allow the cloth to sag in
the middle. When you hold your hands level, the dip will be centered
between them.
|
 |
|
|
|
| Indicating Planes -
Each fold has an upper and l0wer plane with a rounded transition
between them. Also note that the more cloth that is gathered at the
supporting point, the greater the number of folds that appear. |
Placing the Dip - When one point of support is higher than the othr, the dip sits off-center, closer to the lower support. |
|
|
|
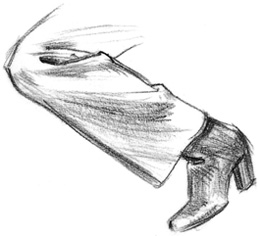
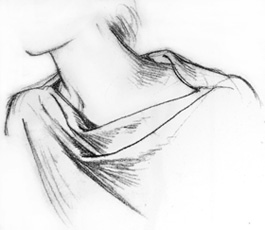
| On the Bias -
Diaper folds on a diagonal bias fall easily and are especially
graceful. To observe diaper folds on the bias, fold your cloth into a
triangle before making them. |
On a Grecian Neckline - Diaper folds fall from this Grecian neckline, a style that has been used for thousands of years and still is seen today. |
|
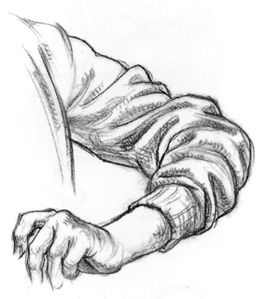
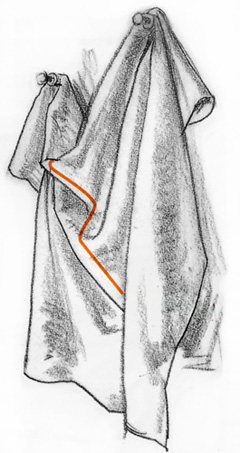
DROP FOLDS
The
characteristic common to all drop folds is that fabric falls freely
from a point or area of support. One simple fold or a complex unit of
folds can fall from an area of support. Manipulating masses of drop
folds gives you so many opportunities to bring life and vitality to your
drawings and enhance their designs that I think of a drop fold as a
gift to an artist.
|
|
|
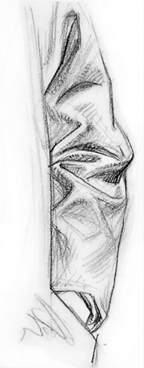
Simple Drop Folds Are Conical -
These simple drop folds that fall from a push pin are conical. You can
bring out this conical quality by showing partial ellipses at the bottom
edges of the folds.
|
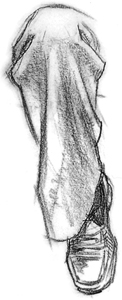 |
Drop Folds Fall From the Knee -
You can almost always see a drop fold falling from the knee of a bent
leg. Half-lock folds at the sides accompany the drop fold.
|
|
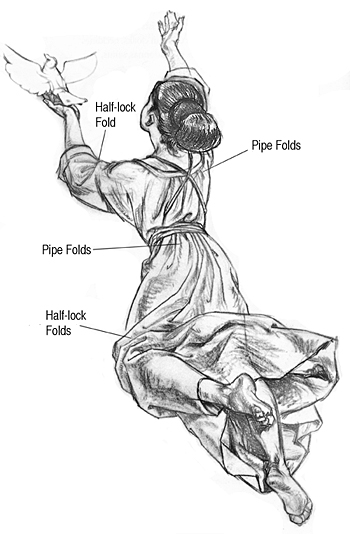
Masses of Fabric Provide Several Useful Types of Folds -
The hanging mass falling free from the sash around the waist of this
figure contains several types of folds, but each of them contributes to
the single dropping arrangement. Such free parts of clothing are
wonderful to use. You can let them fly out to emphasize or create action
in your characters. You can use them to indicate wind and atmosphere.
And you can use them as design elements in your drawing.
|
 |
|
INERT FOLDS
Inert
folds are sometimes called "dead folds," but they can add so much
beauty to a drawing that "inactive" is a more appropriate term. As with
drop folds, a mass of inert folds may contain several other types of
folds, but the entire mass itself is considered inert.
Though
the mass of folds is inert, you can suggest any movement just finished.
In your drawings, you can arrange extra fabric of long garments into
inert folds to suggest any action a character has just taken or the
direction from which a figure has come.
|
|
|
Folds Within an Inert Mass Can Change -
Drop some cloth on the floor, rumpling it first to make sure it shows
some folds. Then pick it up and drop it again. The folds within the mass
change each time, but the mass itself remains inert, not indicating any
movement. |
|
|
|
|
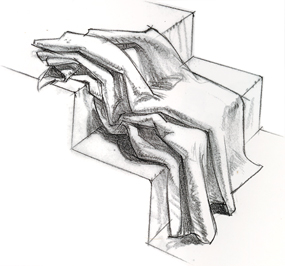
Inert Masses of Folds Reflect the Surface Beneath -
I gathered this fabric at one end before draping it over two steps. The
inert mass reflects the pipe folds that fell before I set the cloth
down and the multiple surfaces over which the cloth lies. If I picked up
the cloth and set it down again, the folds would lie differently, but
the collection of folds would indicate the same form of stairs beneath. |
|
|
Click on image to enlarge..........
|
Try
to create and observe these folds yourself. You can arrange some with a
piece of cloth. Others you can best observe by looking at your own
clothing in a mirror. Look for patterns between similar gestures. Also
observe that the same types of folds look different on different
fabrics.
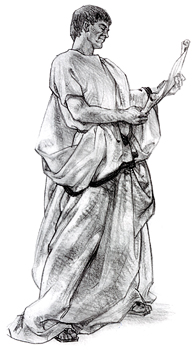
Look for Several Types of Folds
Five of the seven fold types--pipe, half-lock, diaper,
drop and inert--appear in the abundant cloth of this Roman's toga. The
more fabric there is, the more types of folds you'll see.
TYPES OF FOLDS - An Illustrated Tutorial from "Drawing People: How to Portray the Clothed Figure"
by Barbara Bradley
1927-2008
- Recognized as one of the best and most inspiring teachers of drawing
in the country. She was an award winning illustrator, instructor, and
painter. She was also the Director of the School of Illustration at the
Academy of Art University in San Francisco for twenty-five years.
She
was one of a handful of successful women in a male-dominated
profession, although she didn't consider herself a pioneer; she merely
did what she loved to do.
|